Introduction:
The gallbladder, a small organ situated below the liver, plays a crucial role in our digestion process. It stores and concentrates bile, a digestive fluid produced by the liver, and releases it when we consume fatty foods. However, like any other organ in our body, the gallbladder is also prone to certain health problems that can impact our digestion and overall health. In this blog post, we’ll take a closer look at the gallbladder anatomy, its function, and common problems associated with it. We’ll also discuss various treatments available for these conditions.
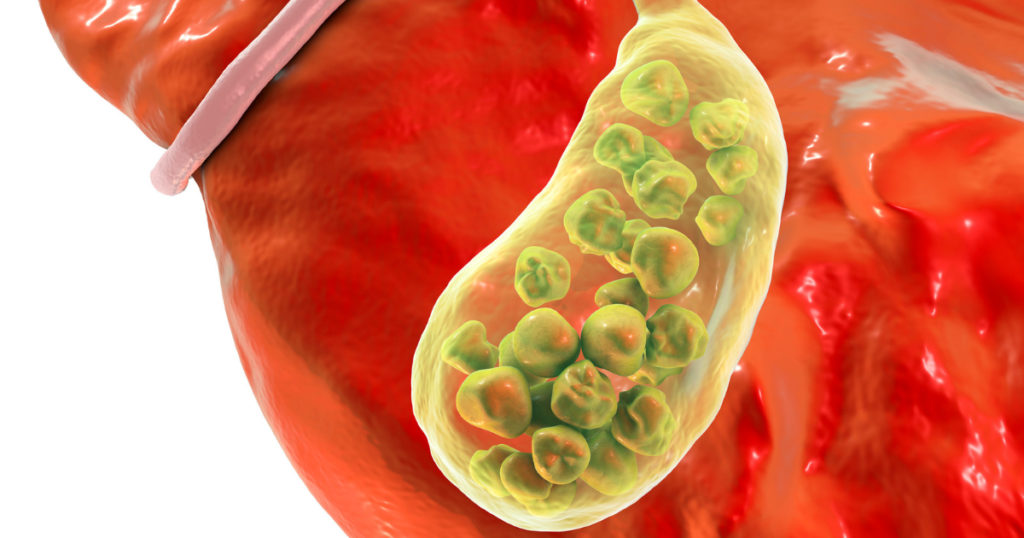
Anatomy of the Gallbladder:
The gallbladder is a pear-shaped organ that measures around 3-4 inches in length. It is divided into three main parts – the fundus (body), neck, and infundibulum (cystic sac). The cystic duct connects the gallbladder to the common bile duct, which further drains into the small intestine. The hepatic ducts are responsible for carrying bile from the liver to the gallbladder. The combined duct system is essential for ensuring that bile flows properly and helps with fat digestion.

Functions of the Gallbladder:
The major function of the gallbladder is to store and concentrate bile produced by the liver. Bile contains bile salts, cholesterol, and waste products that help in the digestion of fats in our diet. When we consume a fatty meal, the gallbladder contracts and releases the stored bile into the small intestine. The bile emulsifies the fats, making it easier for the enzymes in the pancreas to break them down. The gallbladder also helps in removing waste substances from the blood, such as bilirubin, a pigment produced by the breakdown of red blood cells.
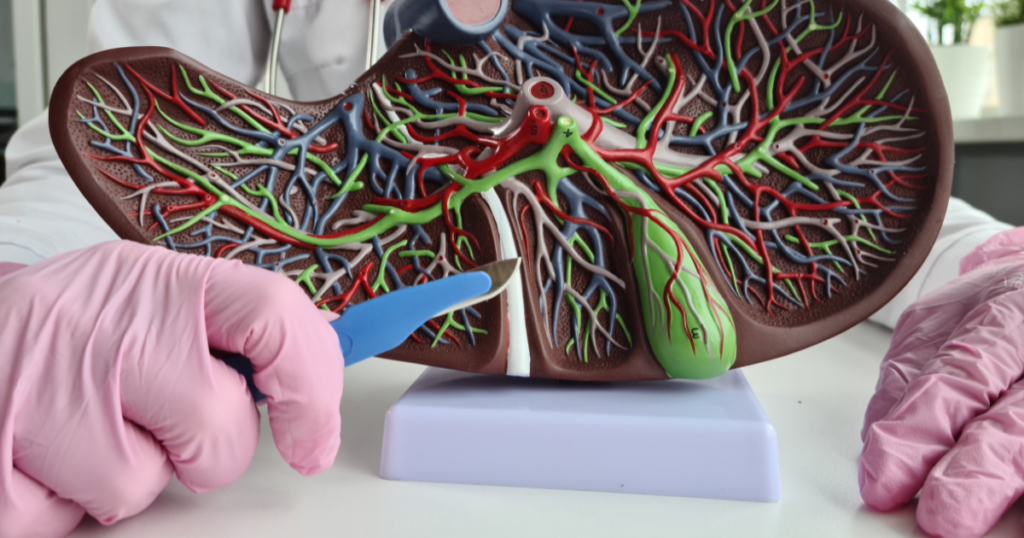
Common Problems Affecting the Gallbladder:
Several factors can cause health problems that affect the functioning of the gallbladder. Gallstones are one of the most common issues that affect the gallbladder. These are small, hard deposits that form in the gallbladder, usually consisting of cholesterol or bilirubin. Gallstones can cause severe pain in the upper abdomen, nausea, and vomiting.
Cholecystitis, an inflammation of the gallbladder, can also cause severe abdominal pain, fever, and jaundice. It can be acute or chronic, and in some cases, may lead to the need for surgery to remove the gallbladder.
Acalculous cholecystitis is when the inflammation occurs without gallstones. This is a rare condition and is more common in people who are critically ill or have had surgery.
Biliary dyskinesia occurs when the muscle of the gallbladder does not function correctly. This condition can cause pain in the right upper quadrant, bloating, nausea, and vomiting.
Lastly, the gallbladder can also develop polyps or cancer. These conditions may require surgery or other treatments to address the problem and prevent further complications.
Treatments for Gallbladder Problems:
Treatment for gallbladder problems varies depending on the specific condition. For gallstones, oral dissolution therapy involves taking medication to dissolve the stones. However, if the stones are too large or painful, cholecystectomy may be necessary. This is a surgical procedure that involves removing the gallbladder through a small incision in the abdomen (laparoscopic), or a larger incision (open).

In some cases, a procedure called ERCP (endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography) might be required. It involves using an endoscope to view the bile ducts and gallbladder and may involve the removal of gallstones or polyps. For further health diseases visit blog.
Conclusion:
The gallbladder plays a crucial role in our digestion process, and any issues affecting it can cause serious health problems. Knowing the anatomy, functions, and common problems associated with it can help you better understand any issues you may experience. Treatments vary, depending on your specific condition and its severity, but can include surgery or medication to dissolve gallstones. If you suspect you have any gallbladder issues, it’s essential to talk to your healthcare provider to receive prompt treatment and restore your digestive system’s functionality.